Best Gastric Balloon Procedure
About Gastric Balloon Procedure
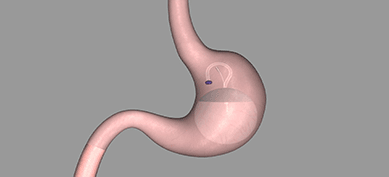
This is a day procedure wherein an endoscope introduces a deflated balloon into the stomach via the oral route. The balloon is then inflated and deployed, and the endoscope is removed. By doing this 2/3 rd of the stomach is filled, thus creating satiety and restricting oral intake, inducing weight loss.
The gastric balloon is a non-surgical weight loss procedure. It has emerged as a boon for this section of overweight, class 1, and class 2 obese people who have tried exercising and dieting, lifestyle modifications, and for those who are not good candidates or do not wish to undergo weight loss surgery. However, even though it is a simple procedure, one must be eligible for the gastric balloon. A prior endoscopy is essential before the balloon procedure, and it should be expected to ensure the safe placement of the intra-gastric balloon.
Procedure: The gastric balloon is silicone and inserted into the stomach endoscopically deflated. The balloon is then inflated with saline and methylene blue and dislodged in the stomach, which stays for six months to a year or more before removal.
The balloon inflation should be adequate to achieve its purpose of weight loss and avoid the risk of it passing through the pylorus. The methylene dye is used to alert the patients of any leak of the saline from the balloon, which could occur and will be noticed as a blue color in the urine. This needs to be informed to the doctor immediately so that necessary intervention and removal of the balloon can be made to avoid complications. The entire process may take up to 30 minutes and is done under sedation/anesthesia.
Mechanism of achieving the goal: As the average gastric volume is around 900ml approximately, the gastric balloon may be inflated up to 500 to 550 ml to occupy space in the stomach to induce fullness or satiety, reduce hunger bouts and intake of food, and delay gastric emptying (the process of moving the contents of the stomach into the duodenum for further absorption). These factors form the cornerstone of weight shedding, the main objective of the Gastric Balloon procedure.
The Gastric Balloon Comes in Three Types.
A balloon is inserted endoscopically, which can stay in the stomach for 6 months( during which weight loss is to be achieved), and then is removed endoscopically.
As the name suggests, the balloon is adjustable, which means that the size of the balloon, after placing it in the stomach endoscopically, can be increased when further weight loss is required by increasing the restriction of food intake. Similarly, if the person feels uncomfortable after the balloon procedure with the amount of saline inflated, removing a few ml of saline can make the person comfortable. This adjustment is made endoscopically by the doctor
The non-endoscopic gastric balloon comes in the form of a capsule that must be swallowed for placement in the stomach. Once inside the stomach and position is confirmed radiographically by the C arm, it is inflated with saline and dislodged from the source. It stays in the stomach in the inflated condition for four months, after which it empties itself and is naturally excreted.
Post Procedural care: The individual may experience teething problems, including cramps and stomach nausea until it adjusts with the inflated gastric balloon. A liquid or soft diet for a couple of weeks may exhibit promising results, followed by embracing healthy diets.
Safety: The gastric balloon is very safe and rarely encounters any complications. The risks that are only presumed to occur are esophageal ulcers or perforation as part of procedure complications, rupture of balloon causing the dye to release in the urine, or deflation of the balloon leading to blockage in the intestine.